1. Servo Motors: “Precision Control Experts” in Industrial Automation Scenarios
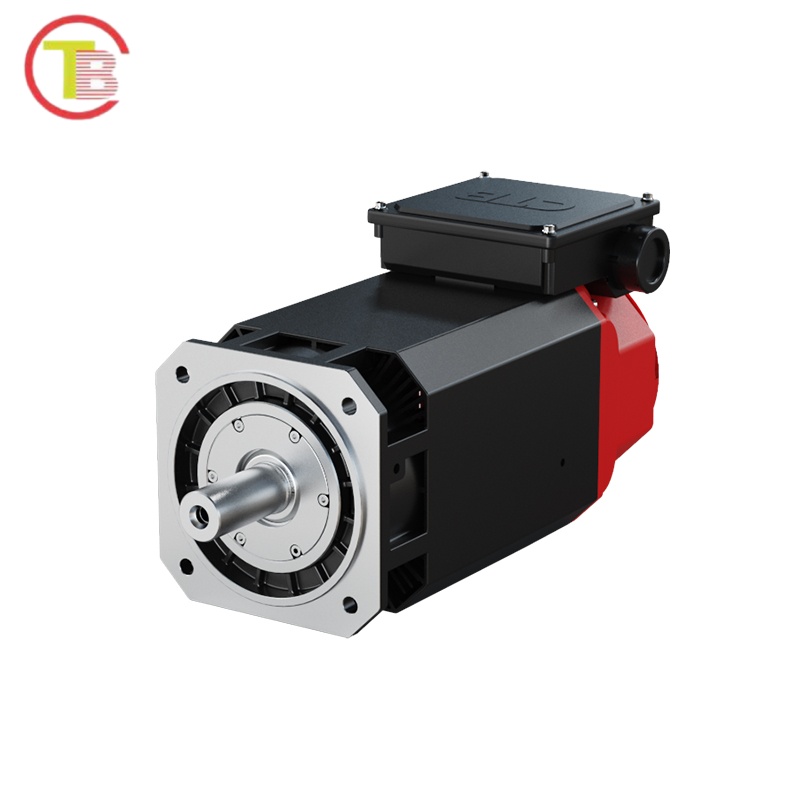

In the field of precision manufacturing, servo motors stand out as core power sources due to their dual advantages of “high precision and high dynamic response”. Equipped with a 17-bit absolute encoder, they can achieve a positioning accuracy of ±0.001mm, meeting the “micron-level processing” requirements of CNC machine tools and precision assembly robots. Meanwhile, with a torque response time of less than 0.5ms and an overload capacity of 200% for 3 seconds, they can quickly handle high-frequency start-stop and forward-reverse switching of equipment. Even for high-speed sorting machines with 3,000 operation commands per hour, they can execute accurately without lag, effectively solving the problem of production loss caused by large positioning errors and slow operation of traditional motors.
2. Three-Phase AC Motors: “Versatile Workhorses” in General Industrial Scenarios
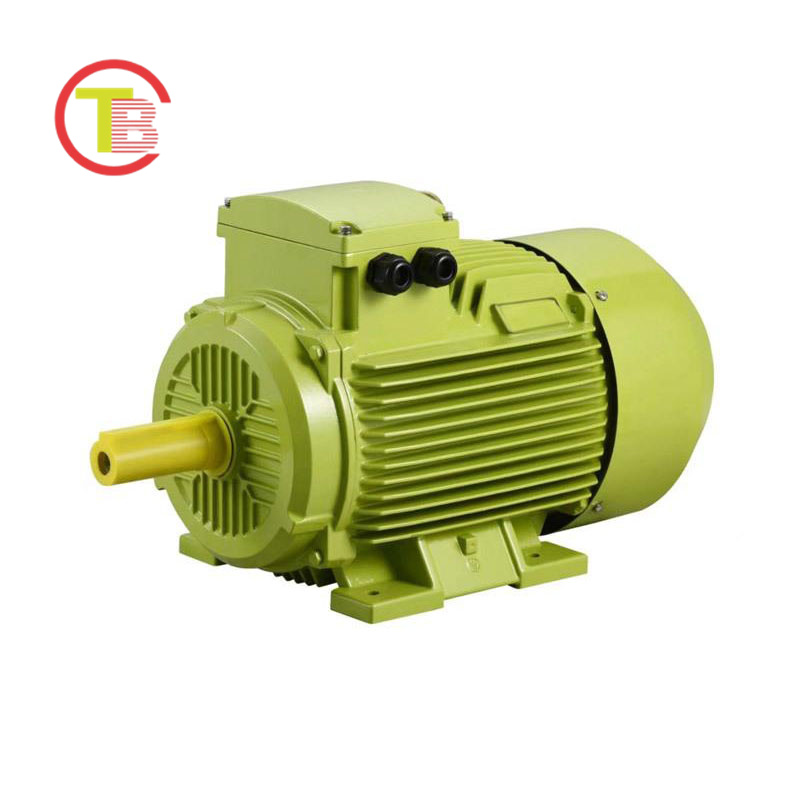

Three-phase AC motors are widely used in general industrial fields such as textile mills, water treatment plants, and logistics warehouses, thanks to their “strong adaptability and low maintenance costs”. Their simple and robust structure—without complex electronic control components—enables them to operate stably in dusty or moderately humid environments, such as driving conveyor belts in logistics warehouses or water pumps in water treatment systems. With a power range covering 0.75kW to 1000kW, they can be flexibly matched to different load demands, from small textile machines to large air compressors. Additionally, their mature manufacturing technology leads to low failure rates, with average maintenance intervals extending to 2-3 years, significantly reducing the daily maintenance workload and costs for enterprises compared to motors with complex structures.
If you need to add application details of three-phase AC motors in specific industries (such as textiles or logistics) or adjust the English expression of technical parameters, I can further optimize this supplementary English content for three-phase AC motors for you. Would you like that?
3. Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors (PMSMs): “Efficient and Energy-Saving Core” in New Energy Vehicle Scenarios
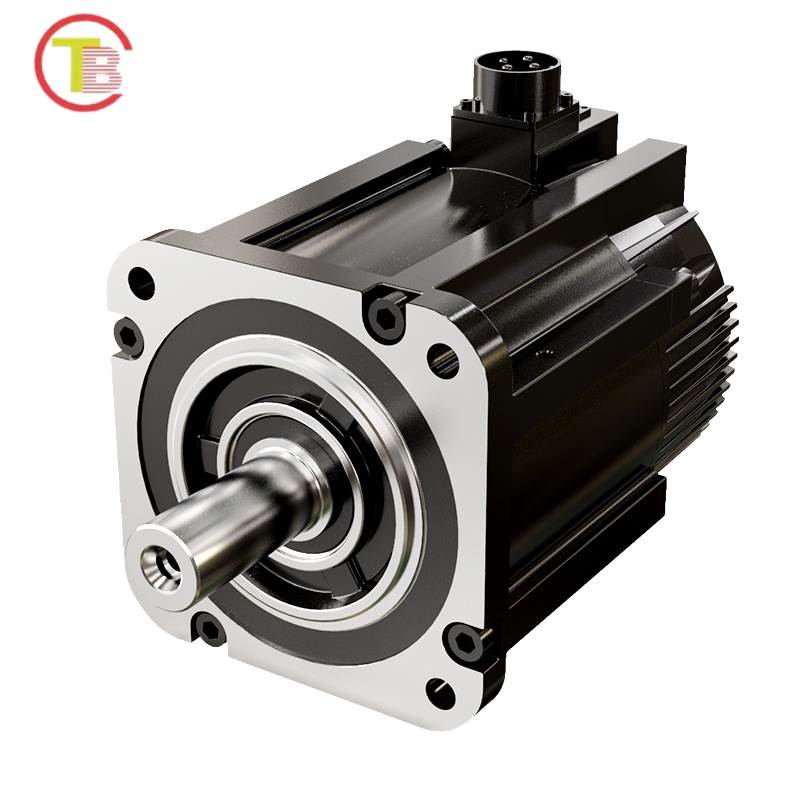

In the drive systems of new energy vehicles, PMSMs have become the mainstream choice due to their advantages of “high energy efficiency and high power density”. Using rare-earth permanent magnet materials, they meet the IE5 ultra-high energy efficiency standard, reducing energy consumption by 15% compared to asynchronous motors during high-speed driving. When combined with the vehicle’s electronic control system, they can increase the driving range by 8%-12%. Moreover, their power density reaches 3kW/kg, and their volume is 20% smaller than that of motors with the same power, allowing flexible adaptation to the limited installation space in the vehicle chassis. With an operating noise below 65 decibels, they balance the vehicle’s dynamic performance, range, and riding comfort.
4. Medium and High-Voltage Motors: “Heavy-Duty Stability Leaders” in Heavy Industry Scenarios
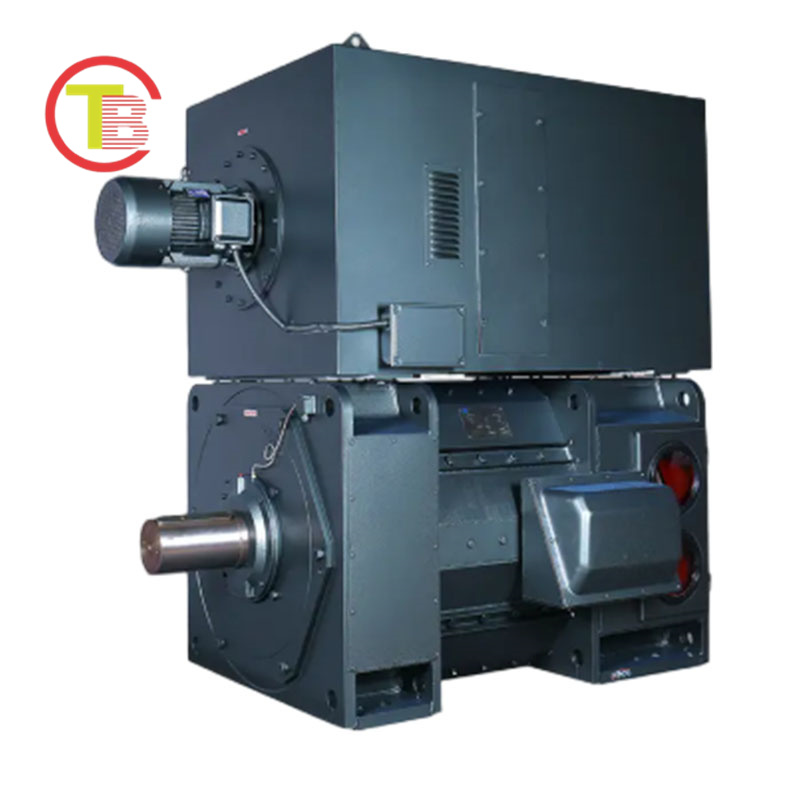
In heavy industry fields such as mining, chemical engineering, and large-scale power generation, medium and high-voltage motors (with voltage levels of 6kV-10kV) are well-suited for high-load production needs due to their “high load-bearing capacity and strong stability”. Adopting reinforced stator windings and high-voltage insulation structures, they can withstand voltage surges of 1.2 times the rated voltage. In equipment that operates continuously for 24 hours, such as mining ball mills and chemical reactors, their MTBF exceeds 30,000 hours, reducing the frequency of shutdowns for maintenance. Furthermore, through optimized electromagnetic design, they save 8%-10% more energy than ordinary low-voltage motors when driving heavy-load equipment like large fans and water pumps. Based on a single motor with a power of 2,000kW and annual operation of 8,000 hours, it can save over 100,000 yuan in electricity costs annually, balancing heavy-load requirements and long-term energy consumption cost control.

